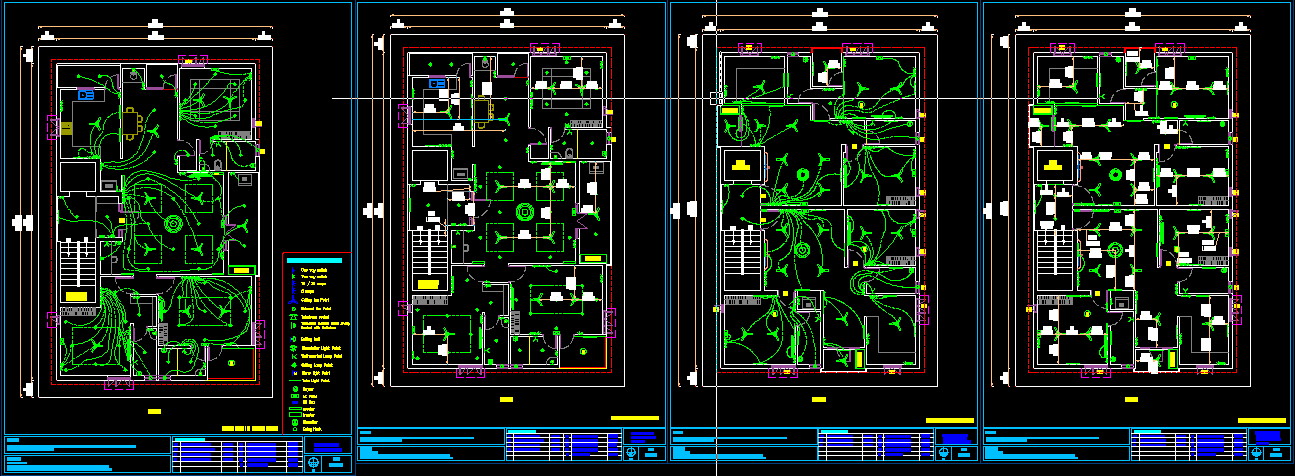
Housing Electrical layout: A building electrical layout is a crucial component of architectural and construction plans. It shows how electrical systems, outlets, wiring, lighting, and other electrical elements are distributed throughout a building. The layout is designed to ensure the safety, functionality, and efficiency of the electrical systems. Here are some of the key uses and purposes of a building electrical layout: 1. Power Distribution Circuit Design: The electrical layout shows the distribution of electrical circuits throughout the building, indicating where power panels, subpanels, and breakers are located. It ensures that electrical loads are balanced across the system to prevent overloading. Electrical Supply: It outlines the routes for power supply from the utility source (like the main electric meter) to various areas of the building, ensuring that each section of the building receives the required power. 2. Lighting Design Light Fixtures Placement: The electrical layout specifies the locations of light fixtures, switches, and outlets. It helps ensure proper illumination, both for general lighting and task-specific lighting (e.g., in kitchens, workspaces). Emergency Lighting: Emergency lighting plans, including exit signs and backup lighting, are part of the layout to meet safety codes. 3. Safety and Code Compliance Adherence to Electrical Codes: The layout ensures that all electrical installations comply with local building codes and national standards (e.g., NEC in the U.S.). It shows proper grounding, circuit protection (such as circuit breakers), and correct placement of outlets and switches to avoid fire hazards or electric shocks. Circuit Protection: It shows where safety devices like circuit breakers or fuses are installed to protect electrical systems and occupants from faults or overloads. 4. Energy Efficiency Efficient Layout of Appliances: By properly positioning outlets, lighting, and appliances, an electrical layout can reduce the need for long extension cords and optimize energy consumption. Energy-Efficient Devices: The layout might include areas for energy-efficient equipment (such as LED lighting, smart thermostats, or energy-saving appliances) to help reduce the building's overall energy consumption. 5. Automation and Smart Systems Home Automation: Many modern buildings incorporate home automation systems (smart homes), which require specific planning in the electrical layout. This includes wiring for devices like smart thermostats, voice-controlled lighting, and security systems. Integration of Security Systems: The layout may also indicate where cameras, motion detectors, alarm systems, and other security elements are wired into the electrical system. 6. HVAC and Other Mechanical Systems HVAC Wiring: Electrical layouts show how heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are powered. This includes wiring for thermostats, motors, fans, and compressors. Other Systems: If the building uses other mechanical systems, such as pumps, water heaters, or elevators, the electrical layout will indicate how they are powered and where the connections are located. 7. Outlets and Switch Placement Convenience and Functionality: The layout shows the precise locations of power outlets, light switches, and electrical devices. This ensures that outlets are placed where they are needed, whether near desks, kitchen appliances, or entertainment systems. Specialty Outlets: It also identifies specialized outlets for high-power devices like ovens, air conditioners, and washers, ensuring they have the right voltage and capacity. 8. Telecommunications and Data Wiring Data Lines and Cables: For commercial or modern residential buildings, the electrical layout often incorporates space for data wiring (e.g., Ethernet cables) and telecommunications systems (such as telephone lines and Wi-Fi routers). Audio/Visual Systems: Some layouts include provisions for multimedia systems, including wiring for speakers, projectors, home theater systems, and other AV setups. 9. Electrical Panel Placement Panel Location: The electrical layout shows the location of the main electrical panel, sub-panels, and any other distribution equipment. It ensures easy access for maintenance and upgrades while adhering to safety standards. Load Distribution: It provides a clear view of how electricity will be routed to various parts of the building, helping to balance electrical loads effectively across the building. 10. Future Expansion Planning for Growth: Electrical layouts often account for future expansion or additions, like extra outlets or additional circuits, to accommodate future electrical needs without requiring a complete redesign of the electrical system. Capacity Planning: The layout helps plan for adequate electrical capacity for future appliances or devices that may be added, ensuring that the electrical system can handle the growing demands of the building. 11. Maintenance and Troubleshooting Ease of Maintenance: An electrical layout is a reference document that helps electricians, contractors, and building owners troubleshoot electrical issues. It can help them quickly locate problems such as a tripped breaker or a faulty connection. Documentation for Inspections: The layout serves as a record for inspections, repairs, or future upgrades, providing a detailed map of the entire electrical system. 12. Coordination with Other Systems Integration with Plumbing, HVAC, and Other Systems: Electrical layouts are often coordinated with other building systems (plumbing, mechanical, and architectural plans). This helps avoid interference between systems, such as electrical wires running too close to water pipes or HVAC ducts. 13. Sustainability and Green Design Renewable Energy Systems: For buildings incorporating renewable energy systems like solar panels or wind turbines, the electrical layout will include the integration of these energy sources into the building’s electrical system. Energy Monitoring: The layout might also include provisions for energy monitoring systems that track the building's energy use, helping reduce waste and improve energy efficiency. In summary, the building electrical layout is a foundational plan that ensures the safe, efficient, and effective distribution of electrical power, supports the building’s functionality, and complies with legal and safety standards. It’s used by architects, engineers, electricians, and contractors throughout the construction and maintenance phases of a building's life. www.bechennai.com
Chat with us on WhatsApp
×
This is your website preview.
Currently it only shows your basic business info. Start adding relevant business details such as description, images and products or services to gain your customers attention by using Boost 360 android app / iOS App / web portal.
Housing Electrical layout: A building electri...
2024-12-31T12:31:53
Housing Electrical layout: A building electrical layout is a crucial component of architectural and construction plans. It shows how electrical systems, outlets, wiring, lighting, and other electrical elements are distributed throughout a building. The layout is designed to ensure the safety, functionality, and efficiency of the electrical systems. Here are some of the key uses and purposes of a building electrical layout: 1. Power Distribution Circuit Design: The electrical layout shows the distribution of electrical circuits throughout the building, indicating where power panels, subpanels, and breakers are located. It ensures that electrical loads are balanced across the system to prevent overloading. Electrical Supply: It outlines the routes for power supply from the utility source (like the main electric meter) to various areas of the building, ensuring that each section of the building receives the required power. 2. Lighting Design Light Fixtures Placement: The electrical layout specifies the locations of light fixtures, switches, and outlets. It helps ensure proper illumination, both for general lighting and task-specific lighting (e.g., in kitchens, workspaces). Emergency Lighting: Emergency lighting plans, including exit signs and backup lighting, are part of the layout to meet safety codes. 3. Safety and Code Compliance Adherence to Electrical Codes: The layout ensures that all electrical installations comply with local building codes and national standards (e.g., NEC in the U.S.). It shows proper grounding, circuit protection (such as circuit breakers), and correct placement of outlets and switches to avoid fire hazards or electric shocks. Circuit Protection: It shows where safety devices like circuit breakers or fuses are installed to protect electrical systems and occupants from faults or overloads. 4. Energy Efficiency Efficient Layout of Appliances: By properly positioning outlets, lighting, and appliances, an electrical layout can reduce the need for long extension cords and optimize energy consumption. Energy-Efficient Devices: The layout might include areas for energy-efficient equipment (such as LED lighting, smart thermostats, or energy-saving appliances) to help reduce the building's overall energy consumption. 5. Automation and Smart Systems Home Automation: Many modern buildings incorporate home automation systems (smart homes), which require specific planning in the electrical layout. This includes wiring for devices like smart thermostats, voice-controlled lighting, and security systems. Integration of Security Systems: The layout may also indicate where cameras, motion detectors, alarm systems, and other security elements are wired into the electrical system. 6. HVAC and Other Mechanical Systems HVAC Wiring: Electrical layouts show how heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are powered. This includes wiring for thermostats, motors, fans, and compressors. Other Systems: If the building uses other mechanical systems, such as pumps, water heaters, or elevators, the electrical layout will indicate how they are powered and where the connections are located. 7. Outlets and Switch Placement Convenience and Functionality: The layout shows the precise locations of power outlets, light switches, and electrical devices. This ensures that outlets are placed where they are needed, whether near desks, kitchen appliances, or entertainment systems. Specialty Outlets: It also identifies specialized outlets for high-power devices like ovens, air conditioners, and washers, ensuring they have the right voltage and capacity. 8. Telecommunications and Data Wiring Data Lines and Cables: For commercial or modern residential buildings, the electrical layout often incorporates space for data wiring (e.g., Ethernet cables) and telecommunications systems (such as telephone lines and Wi-Fi routers). Audio/Visual Systems: Some layouts include provisions for multimedia systems, including wiring for speakers, projectors, home theater systems, and other AV setups. 9. Electrical Panel Placement Panel Location: The electrical layout shows the location of the main electrical panel, sub-panels, and any other distribution equipment. It ensures easy access for maintenance and upgrades while adhering to safety standards. Load Distribution: It provides a clear view of how electricity will be routed to various parts of the building, helping to balance electrical loads effectively across the building. 10. Future Expansion Planning for Growth: Electrical layouts often account for future expansion or additions, like extra outlets or additional circuits, to accommodate future electrical needs without requiring a complete redesign of the electrical system. Capacity Planning: The layout helps plan for adequate electrical capacity for future appliances or devices that may be added, ensuring that the electrical system can handle the growing demands of the building. 11. Maintenance and Troubleshooting Ease of Maintenance: An electrical layout is a reference document that helps electricians, contractors, and building owners troubleshoot electrical issues. It can help them quickly locate problems such as a tripped breaker or a faulty connection. Documentation for Inspections: The layout serves as a record for inspections, repairs, or future upgrades, providing a detailed map of the entire electrical system. 12. Coordination with Other Systems Integration with Plumbing, HVAC, and Other Systems: Electrical layouts are often coordinated with other building systems (plumbing, mechanical, and architectural plans). This helps avoid interference between systems, such as electrical wires running too close to water pipes or HVAC ducts. 13. Sustainability and Green Design Renewable Energy Systems: For buildings incorporating renewable energy systems like solar panels or wind turbines, the electrical layout will include the integration of these energy sources into the building’s electrical system. Energy Monitoring: The layout might also include provisions for energy monitoring systems that track the building's energy use, helping reduce waste and improve energy efficiency. In summary, the building electrical layout is a foundational plan that ensures the safe, efficient, and effective distribution of electrical power, supports the building’s functionality, and complies with legal and safety standards. It’s used by architects, engineers, electricians, and contractors throughout the construction and maintenance phases of a building's life. www.bechennai.com
2024-12-31T12:31:53
Keywords
- located 7 outlets
- maintenance phases
- architectural plans
- inspections repairs
- ethernet cables
- precise locations
- construction plans
- building 11 maintenance
- highpower devices
- safety devices
- effective distribution
- extra outlets
- distribution equipment
- circuit breakers
- safety functionality
- layout ensures
- data wiring
- includes wiring
- energysaving appliances
- buildings functionality
- safety standards
- safe efficient
- wind turbines
- plumbing hvac
- detailed map
- tripped breaker
- reference document
- troubleshooting ease
- growing demands
- added ensuring
- complete redesign
- additional circuits
- clear view
- telephone lines
- incorporates space
- washers ensuring
- heating ventilation
- energyefficient equipment
- national standards
- backup lighting
- exit signs
- taskspecific lighting
- general lighting
- utility source
- crucial component
- electrical system
- layout serves
- layout shows
- building receives
- building ensuring
- building indicating
- electrical devices
- systems integration
- multimedia systems
- telecommunications systems
- mechanical systems
- future appliances
- security elements
- foundational plan
- energy sources
- solar panels
- water pipes
- future expansion
- capacity 8 telecommunications
- security systems
- correct placement
- electrical loads
- electrical circuits
- electrical elements
- building helping
- electrical layout
- power supply
- electrical systems
- buildings energy
- electrical codes
- security systems integration
- electrical layout shows
- building electrical layout
- systems electrical layouts
- helping reduce waste
- improve energy efficiency
- future upgrades providing
- layout helps plan
- ensures easy access
- local building codes
- electrical layout specifies
- housing electrical layout
- energy monitoring systems
- identifies specialized outlets
- protect electrical systems
- desks kitchen appliances
- growth electrical layouts
- helps electricians contractors
- light fixtures switches
- adequate electrical capacity
- accommodate future electrical
- power panels subpanels
- electrical power supports
- buildings life wwwbechennaicom
- modern residential buildings
- switch placement convenience
- pumps water heaters
- electrical wires running
- electrical installations comply
- architects engineers electricians
- helps avoid interference
- faulty connection documentation
- quickly locate problems
- ovens air conditioners
- thermostats motors fans
- require specific planning
- long extension cords
- avoid fire hazards
- code compliance adherence
- main electric meter

Submit Your Enquiry