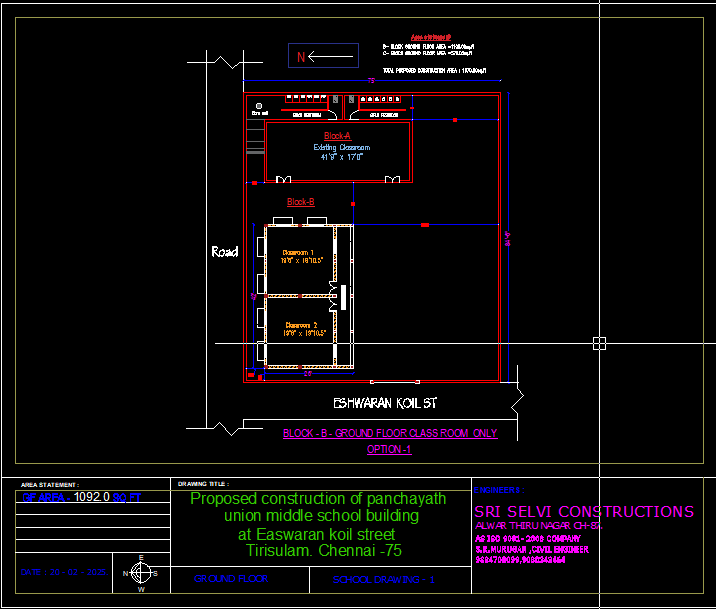
School building plan : Reating a school building plan involves several key components that ensure functionality, safety, accessibility, and an environment conducive to learning. Here's a breakdown of the main aspects to consider when designing a school building plan: 1. Site Planning and Layout Location and Accessibility: The school should be located in a place that is easily accessible by roads, public transport, and safe walking paths. Consider proximity to residential areas and surrounding infrastructure. Zoning and Compliance: Ensure the land is zoned for educational purposes and that the building plan adheres to local building codes, regulations, and zoning laws. Safety and Security: Create clear access points, proper fencing, and secure areas to minimize security risks. Entrances and exits should be well-marked and wide enough for easy evacuation in case of an emergency. Parking and Drop-off Zones: Design adequate parking for staff and visitors, as well as safe areas for student drop-offs and pickups. 2. Building Zones and Functional Spaces Classrooms: These should be the central part of the school plan. Each classroom must have proper lighting, ventilation, and acoustic treatment. Consider flexibility in classroom size to accommodate different teaching styles. Size: Standard classrooms typically range from 600–800 sq. ft. for elementary and around 800–1, 000 sq. ft. for high school classrooms. Furniture Layout: Ensure space for desks, teacher's area, and storage. Specialty Rooms: Science Labs: Equipped with sinks, lab tables, and safety equipment. Art and Music Rooms: Large, open spaces with proper ventilation for art supplies or music instruments. Computer Labs: Well-ventilated spaces with sufficient power outlets for computers, projectors, and other tech equipment. Libraries: A central hub for reading and studying. A combination of quiet spaces for reading and areas for group learning should be incorporated. Restrooms: Adequate numbers of student and staff restrooms should be planned. These should be designed for easy cleaning and include separate facilities for boys and girls. Consider accessibility for students with disabilities. Cafeteria: A spacious, well-ventilated area for dining, which should be large enough to accommodate all students during break times. Multipurpose Rooms or Auditoriums: These rooms can be used for assemblies, events, sports activities, or group classes. Admin Offices: The principal’s office, staff rooms, and other administrative areas should be centrally located and easily accessible. Storage Areas: Include storage for supplies, janitorial items, and sports equipment. Health Room: A first aid room or nurse's office for students who need medical attention. 3. Building Design and Structure Open Layout vs. Closed Spaces: Schools should have a mix of open and closed spaces. Open areas allow for social interaction, while closed classrooms are essential for focused learning. Accessibility: Include ramps, wider doorways, and elevators (if multiple floors) for students and staff with disabilities. Natural Light: Maximize daylight with large windows or skylights. Proper lighting is crucial for creating a pleasant learning environment. Ventilation and Air Quality: Ensure proper air circulation, and consider energy-efficient systems for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC). Safety and Fire Exits: Clearly marked emergency exits and fire escape routes are essential. The building should have fire alarms, extinguishers, and sprinklers installed throughout. 4. Outdoor Spaces Playgrounds: For younger students, a safe playground with age-appropriate equipment is essential. Sports Fields: A space for sports activities such as soccer, basketball, and track & field. Gardens or Green Spaces: These can serve as calming areas for students to relax during breaks. Parking Lots: Safe and efficient spaces for staff and visitor parking. Walkways: Safe pedestrian paths around the school for students to navigate easily. 5. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Energy-Efficient Design: Use of insulation, solar panels, energy-efficient HVAC systems, and LED lighting can make the school more sustainable and reduce operational costs. Rainwater Harvesting: Implementing rainwater collection systems for irrigation purposes or other non-potable uses. Green Building Materials: Use eco-friendly, non-toxic materials such as bamboo flooring, low-VOC paints, and recycled materials to construct the building. Natural Cooling and Heating: Passive design strategies like cross-ventilation and shading devices can reduce energy consumption. 6. Technology Infrastructure IT and Electrical Wiring: Plan for a network of internet cables, electrical outlets, and power sources for tech tools in every classroom and specialty room. Security Systems: CCTV cameras and electronic access systems can help monitor the school’s premises for safety. 7. Compliance with Standards and Regulations Fire Safety Codes: Follow local fire safety regulations, including clear exits, fire alarms, sprinkler systems, and fire-resistant building materials. Accessibility Standards: Adhere to local and international accessibility standards like the ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) to ensure the school is accessible to all students. Health Codes: Make sure the design meets public health codes, including proper sanitation facilities and food safety in the cafeteria. 8. Interior Design Color Scheme: Use bright, inviting colors for classrooms and public spaces that promote focus and creativity. Acoustics: Design classrooms with soundproofing materials to reduce noise distractions, especially in multipurpose rooms and auditoriums. Furniture: Include adjustable desks and chairs to accommodate various learning styles, ages, and activities. 9. Sample Building Zones First Floor: Administrative offices, staff room, classrooms, cafeteria, gymnasium, multipurpose hall. Second Floor: More classrooms, science labs, art/music rooms, computer labs, libraries. Outdoor: Playground, sports fields, gardens, parking. 10. Future Expansion Modular Design: Leave room for the future expansion of classrooms or facilities as student enrollment increases. Flexible Spaces: Design some spaces with the possibility of changing their use over time as educational needs evolve. Mobile no:888 333 33 22. www.bechennai.com.
Chat with us on WhatsApp
×
This is your website preview.
Currently it only shows your basic business info. Start adding relevant business details such as description, images and products or services to gain your customers attention by using Boost 360 android app / iOS App / web portal.
School building plan : Reating a school buildi...
2025-02-25T13:13:13
School building plan : Reating a school building plan involves several key components that ensure functionality, safety, accessibility, and an environment conducive to learning. Here's a breakdown of the main aspects to consider when designing a school building plan: 1. Site Planning and Layout Location and Accessibility: The school should be located in a place that is easily accessible by roads, public transport, and safe walking paths. Consider proximity to residential areas and surrounding infrastructure. Zoning and Compliance: Ensure the land is zoned for educational purposes and that the building plan adheres to local building codes, regulations, and zoning laws. Safety and Security: Create clear access points, proper fencing, and secure areas to minimize security risks. Entrances and exits should be well-marked and wide enough for easy evacuation in case of an emergency. Parking and Drop-off Zones: Design adequate parking for staff and visitors, as well as safe areas for student drop-offs and pickups. 2. Building Zones and Functional Spaces Classrooms: These should be the central part of the school plan. Each classroom must have proper lighting, ventilation, and acoustic treatment. Consider flexibility in classroom size to accommodate different teaching styles. Size: Standard classrooms typically range from 600–800 sq. ft. for elementary and around 800–1, 000 sq. ft. for high school classrooms. Furniture Layout: Ensure space for desks, teacher's area, and storage. Specialty Rooms: Science Labs: Equipped with sinks, lab tables, and safety equipment. Art and Music Rooms: Large, open spaces with proper ventilation for art supplies or music instruments. Computer Labs: Well-ventilated spaces with sufficient power outlets for computers, projectors, and other tech equipment. Libraries: A central hub for reading and studying. A combination of quiet spaces for reading and areas for group learning should be incorporated. Restrooms: Adequate numbers of student and staff restrooms should be planned. These should be designed for easy cleaning and include separate facilities for boys and girls. Consider accessibility for students with disabilities. Cafeteria: A spacious, well-ventilated area for dining, which should be large enough to accommodate all students during break times. Multipurpose Rooms or Auditoriums: These rooms can be used for assemblies, events, sports activities, or group classes. Admin Offices: The principal’s office, staff rooms, and other administrative areas should be centrally located and easily accessible. Storage Areas: Include storage for supplies, janitorial items, and sports equipment. Health Room: A first aid room or nurse's office for students who need medical attention. 3. Building Design and Structure Open Layout vs. Closed Spaces: Schools should have a mix of open and closed spaces. Open areas allow for social interaction, while closed classrooms are essential for focused learning. Accessibility: Include ramps, wider doorways, and elevators (if multiple floors) for students and staff with disabilities. Natural Light: Maximize daylight with large windows or skylights. Proper lighting is crucial for creating a pleasant learning environment. Ventilation and Air Quality: Ensure proper air circulation, and consider energy-efficient systems for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC). Safety and Fire Exits: Clearly marked emergency exits and fire escape routes are essential. The building should have fire alarms, extinguishers, and sprinklers installed throughout. 4. Outdoor Spaces Playgrounds: For younger students, a safe playground with age-appropriate equipment is essential. Sports Fields: A space for sports activities such as soccer, basketball, and track & field. Gardens or Green Spaces: These can serve as calming areas for students to relax during breaks. Parking Lots: Safe and efficient spaces for staff and visitor parking. Walkways: Safe pedestrian paths around the school for students to navigate easily. 5. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Energy-Efficient Design: Use of insulation, solar panels, energy-efficient HVAC systems, and LED lighting can make the school more sustainable and reduce operational costs. Rainwater Harvesting: Implementing rainwater collection systems for irrigation purposes or other non-potable uses. Green Building Materials: Use eco-friendly, non-toxic materials such as bamboo flooring, low-VOC paints, and recycled materials to construct the building. Natural Cooling and Heating: Passive design strategies like cross-ventilation and shading devices can reduce energy consumption. 6. Technology Infrastructure IT and Electrical Wiring: Plan for a network of internet cables, electrical outlets, and power sources for tech tools in every classroom and specialty room. Security Systems: CCTV cameras and electronic access systems can help monitor the school’s premises for safety. 7. Compliance with Standards and Regulations Fire Safety Codes: Follow local fire safety regulations, including clear exits, fire alarms, sprinkler systems, and fire-resistant building materials. Accessibility Standards: Adhere to local and international accessibility standards like the ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) to ensure the school is accessible to all students. Health Codes: Make sure the design meets public health codes, including proper sanitation facilities and food safety in the cafeteria. 8. Interior Design Color Scheme: Use bright, inviting colors for classrooms and public spaces that promote focus and creativity. Acoustics: Design classrooms with soundproofing materials to reduce noise distractions, especially in multipurpose rooms and auditoriums. Furniture: Include adjustable desks and chairs to accommodate various learning styles, ages, and activities. 9. Sample Building Zones First Floor: Administrative offices, staff room, classrooms, cafeteria, gymnasium, multipurpose hall. Second Floor: More classrooms, science labs, art/music rooms, computer labs, libraries. Outdoor: Playground, sports fields, gardens, parking. 10. Future Expansion Modular Design: Leave room for the future expansion of classrooms or facilities as student enrollment increases. Flexible Spaces: Design some spaces with the possibility of changing their use over time as educational needs evolve. Mobile no:888 333 33 22. www.bechennai.com.
2025-02-25T13:13:13
Keywords
- younger students
- staff restrooms
- classroom size
- auditoriums furniture
- multipurpose rooms
- large windows
- centrally located
- student dropoffs
- educational purposes
- compliance ensure
- easily accessible
- calming areas
- administrative areas
- secure areas
- residential areas
- school plan
- future expansion
- promote focus
- disabilities act
- ada americans
- shading devices
- irrigation purposes
- soccer basketball
- sprinklers installed
- multiple floors
- social interaction
- nurses office
- aid room
- disabilities cafeteria
- separate facilities
- easy cleaning
- central hub
- computers projectors
- 600800 sq ft
- acoustic treatment
- central part
- easy evacuation
- main aspects
- environment conducive
- key components
- efficient spaces
- quiet spaces
- safe areas
- closed classrooms
- safe playground
- heating ventilation
- adjustable desks
- soundproofing materials
- food safety
- safety 7 compliance
- schools premises
- tech tools
- power sources
- recycled materials
- sports activities
- energyefficient systems
- group learning
- emergency parking
- layout location
- learning heres
- public spaces
- green spaces
- led lighting
- ageappropriate equipment
- fire exits
- art supplies
- proper ventilation
- functional spaces classrooms
- international accessibility standards
- closed spaces schools
- essential sports fields
- green building materials
- marked emergency exits
- focused learning accessibility
- structure open layout
- safety equipment art
- proper sanitation facilities
- proper lighting ventilation
- tech equipment libraries
- building plan adheres
- safe walking paths
- skylights proper lighting
- learning styles ages
- electronic access systems
- building natural cooling
- ecofriendly nontoxic materials
- supplies janitorial items
- sufficient power outlets
- desks teachers area
- zoning laws safety
- roads public transport
- electrical wiring plan
- fire alarms extinguishers
- fire escape routes
- reduce noise distractions
- bright inviting colors
- track field gardens
- ramps wider doorways
- spacious wellventilated area
- sinks lab tables
- surrounding infrastructure zoning

Submit Your Enquiry